The Cruelty You Don't See: The suffering of pet macaques for social media content
Press release
Think that pet monkeys on social media are cute? Think again. Macaques are being abused as pets on social media, and social media platforms are failing to protect them, animal experts warn.
Macaques being kept as pets are being physically and psychologically abused for social media content, states a new report released today.
Compiled by a coalition of 20 animal protection organizations, the report “The cruelty you don't see: The suffering of pet macaques for social media content” documents evidence of content creators openly abusing monkeys on social media sites such as Facebook and YouTube.
The Asia for Animals’ Social Media Animal Cruelty Coalition (SMACC) conducted research into this online trend, which it says is inherently abusive and is being fueled by social media. Between September 2021 and March 2023, SMACC recorded 1226 content links from Facebook, Instagram, TikTok and YouTube, showing macaques kept as pets. The content ranged from seemingly “innocent” treatment to the violent and graphic torture of macaques and collectively had over 12 billion views.
The research found:
- 13% of the content features deliberate psychological torture: macaques were intentionally made to feel fear and distress in response to scaring, teasing and being denied food
- 12% showed macaques being physically tortured, including being beaten, burnt alive, limbs amputated and many of them tortured until death
- Shockingly, 60% of the links showed pet macaques being directly physically abused
- All macaques featured were likely to experience psychological distress due to their treatment.
- Collectively, the links had been viewed 12,054,378,907 times at the time of analysis
- Top three platforms with the most content featuring macaques as pets were Facebook (60%), YouTube (24%), and TikTok (13%).
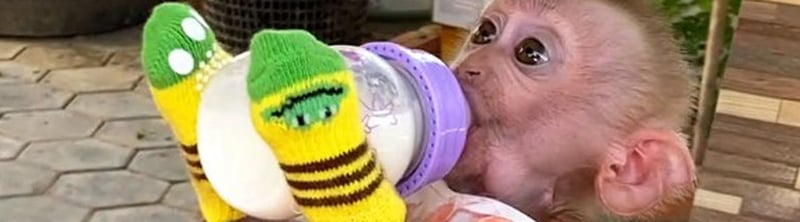
Videos showing monkeys kept in households, dressed in clothing and wearing diapers are popular on social media, with some videos reaching millions of views, and attracting comments on how “cute” and entertaining the content is. This treatment of macaques, usually infants, causes long-lasting physical and psychological damage. Clothing macaques in dresses and shoes causes them discomfort and can restrict their natural movements. In a video found on YouTube with four million views, a monkey is seen with a collared shirt, trousers, shoes, and a backpack. When the monkey walks, they clearly are struggling, as they shuffle their feet and lean from side to side. The video's caption states it was the monkey’s “first day of school.”
Most of the content features infant macaques, who are typically removed from their parents at a very young age, sometimes just days old, in order to be sold into the pet trade. Such maternal and social deprivation can cause severe psychological and emotional damage, including stress and behavioral issues. Macaques may start to perform behaviors known as stereotypies, such as rocking, pacing and overgrooming. Infant macaques can often be seen sucking their fingers in social media content, a coping mechanism that helps them deal with separation and loss.
Nutritional deficiencies in pet primates are also common, with diabetes being seen in many primates kept as pets, due to unsuitable diets. Restrictive environments impact their physical health, and can increase frustration and aggression. When pet monkeys reach maturity, they can become difficult to handle and may even injure their owners. Many end up being rehomed to sanctuaries, or may even be released into the wild where their chance of survival is very low.
Some behaviors exhibited by macaques may be misinterpreted by viewers as positive, but actually the animal is in distress. For example, macaques seen smiling or grinning, are indicating high stress, fear, and aggression.
SMACC stated:
Unfortunately, macaques kept as pets are suffering by the very nature of being kept as a pet, they are not domesticated species like dogs or cats, they are wild animals and their needs cannot be met in a human setting.
SMACC warns that by liking, commenting and sharing this content , viewers are inadvertently supporting their abuse. Popular content is further promoted as engagement grows, motivating content creators to create more. Some may even make money from their content, through monetization on the platform.
Animal experts are also concerned that the ease of which such content is available is normalizing the abuse of macaques, and can lead to the escalation of their abuse. In some content macaques are hit and slapped by their owners to seemingly discipline them. Some creators put the macaques in dangerous situations to film their reactions, or to film themselves rescuing the animal. In a series of videos, baby monkeys can be seen hung from logs in a fast flowing river, in danger of slipping and drowning. Other content creators may intentionally scare or tease their pet macaque, causing fear and distress in order to record their response. Disturbingly, some content creators film the sexual abuse of young macaques, sometimes portrayed as bathing or cleaning of their genitals to appear innocent.
Social media companies need to do more to tackle the problem. Even though some animal-related policies do exist, they are limited and often poorly enforced by platforms.
SMACC reports:
Social media companies are providing a platform for such abuse and therefore have a crucial and pivotal role to play in protecting macaques and other animals. These companies have the power to restrict the hundreds of thousands of creators’ content showing the exploitation and abuse of macaques, through the introduction of key policies and the improvement of manual and automated moderation. They also have a unique opportunity, like no other, to educate their users worldwide on why macaques should not be kept as pets.
World Animal Protection’s Global Head of Wildlife Research, Dr Neil D’Cruze said:
Some of the content shared on social media is incredibly hard to watch. Let’s be clear, this is not entertainment, for ‘likes’ and ‘shares’, this is animal abuse. Many of these videos depict extremely violent content showing the intentional torture and killing of macaques.
Macaques are highly intelligent and social creatures. They form relationships and can remember past interactions, they groom each other as a sign of affection and respect. They think and feel and show emotions. Some of these animals will be living in abject fear and terror.
Social media platforms are normalizing the cruel treatment of macaques by allowing these videos to remain on their platforms. They have a responsibility to shut-down these content creators and send a message that animal cruelty is not to be tolerated. These platforms need to proactively step up and take action to stop animal cruelty content being uploaded in the first place.
If you see this type of content – report it, do not engage with it. We all have a role to play.
SMACC is calling on social media platforms to restrict content which shows macaques as pets, and to take proactive measures to remove content showing their abuse. Social media users are encouraged to not watch or engage with such content, but instead report cruelty content to the platforms.
ENDS
NOTES TO EDITORS
SMACC
The Asia for Animals’ Social Media Animal Cruelty Coalition (SMACC) is composed of twenty well-known and respected animal advocacy organizations who share the aim of stopping the proliferation of animal cruelty content on social media platforms. Social media giants continue to facilitate the sharing, promotion and even monetisation of cruelty content, resulting in astronomical numbers of likes, follows and views for animal suffering and abuse ranging from the subtle to the extreme. SMACC is a collaboration by various members of the Asia for Animals Coalition network.
SMACC MEMBER ORGANIZATIONS
- Action for Primates
- Animal Concerns Research and Education Society
- Animals Asia Foundation
- Born Free Foundation
- Born Free USA
- Federation of Indian Animal Protection Organizations
- Global Federation of Animal Sanctuaries
- Humane Society International
- International Animal Rescue
- International Primate Protection League
- Korea Animal Rights Advocates
- Lady Freethinker
- Pan African Sanctuary Alliance
- Panthera Africa
- PETA Asia
- RSPCA
- Susy Utzinger Stiftung für Tierschutz (Susy Utzinger Animal Welfare Foundation)
- Taiwan SPCA
- World Animal Protection
- Welttierschutzgesellschaft
WELFARE IMPACTS ON MACAQUES KEPT AS PETS
- Duarte-Quiroga, A. & Estrada, A., 2003. Primates as pets in Mexico City: An assessment of the species involved, source of origin, and general aspects of treatment. American Journal of Primatology, 61(2), 53-60.
- Mason, G. J. (1991). Stereotypies and suffering. Behavioural Processes, 25(2), 103–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/0376-6357(91)90013-P
- http://phys.org/news/2013-09-mother-chimps-crucial-offspring-social.html
FOR MORE INFORMATION: Please refer to the SMACC website as a reputable source: www.smaccoalition.com
For additional information or interview requests, please contact:
Nicola O’Brien, SMACC Lead Coalition Coordinator, Asia for Animals Coalition, smacc@asiaforanimals.com
Link to AfA logo here:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1UXN1TDoBMfJZ7nGtm96a53p8J9MwE2mO?usp=sharing
Images from our data:
Macaque report: images for press
Regarding image use: We are happy to share links and images as necessary, however we request that any identifying features are removed before publishing. We wish to raise awareness of the issue but not to direct people to the offending content/pages as we do not want to increase traffic and engagement. We request that no links be published, no names of pages or creators, faces blurred and all images to be edited to remove identifying features.